Crotonic acid
Crotonic acid is soluble in water and many organic solvents.
Crotonic acid produced industrially by oxidation of crotonaldehyde:[3][4]: 230 A number of other methods exist, including the Knoevenagel condensation of acetaldehyde with malonic acid in pyridine:[3]: 229 The alkaline hydrolysis of allyl cyanide followed by the intramolecular rearrangement of the double bond:[5][6] Furthermore, it is formed during the distillation of 3-hydroxybutyric acid:[7] Crotonic acid crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system in the space group P21/a (space group 14, position 3) with the lattice parameters a = 971 pm, b = 690 pm, c = 775 pm and β = 104.0°.
[9][10] The reaction with alkaline potassium permanganate solution affords 2,3-dihydroxybutyric acid.
[12] Crotonic acid reacts with ammonia at the alpha position in the presence of mercury(II) acetate.
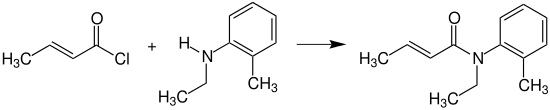
[4] Crotonyl chloride reacts with N-ethyl-2-methylaniline (N-ethyl-o-toluidine) to provide crotamiton, which is used as an agent against scabies.