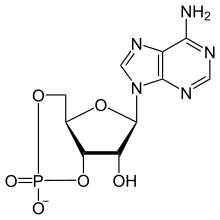
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal transduction in many different organisms, conveying the cAMP-dependent pathway.
cAMP is a second messenger, used for intracellular signal transduction, such as transferring into cells the effects of hormones like glucagon and adrenaline, which cannot pass through the plasma membrane.
cAMP is associated with kinases function in several biochemical processes, including the regulation of glycogen, sugar, and lipid metabolism.
The active subunits catalyze the transfer of phosphate from ATP to specific serine or threonine residues of protein substrates.
The phosphorylated proteins may act directly on the cell's ion channels, or may become activated or inhibited enzymes.
This occurs through inhibition of the cAMP-producing enzyme, adenylate cyclase, as a side-effect of glucose transport into the cell.
CRP-cAMP increases expression of a large number of genes, including some encoding enzymes that can supply energy independent of glucose.
[9] cAMP is involved in activation of trigeminocervical system leading to neurogenic inflammation and causing migraine.
They can be subgrouped into two distinct categories:[11] Forskolin is commonly used as a tool in biochemistry to raise levels of cAMP in the study and research of cell physiology.