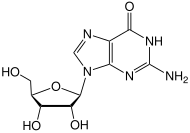
Guanosine
Guanosine (symbol G or Guo) is a purine nucleoside comprising guanine attached to a ribose (ribofuranose) ring via a β-N9-glycosidic bond.
These forms play important roles in various biochemical processes such as synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, photosynthesis, muscle contraction, and intracellular signal transduction (cGMP).
Guanosine is a white, crystalline powder with no odor and mild saline taste.
[3] Guanosine is required for an RNA splicing reaction in mRNA, when a "self-splicing" intron removes itself from the mRNA message by cutting at both ends, re-ligating, and leaving just the exons on either side to be translated into protein.
Guanosine can be found in pancreas, clover, coffee plant, and pollen of pines.