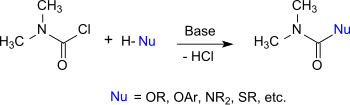Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride
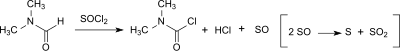
The reaction can also be carried out at the laboratory scale with diphosgene or triphosgene and an aqueous dimethylamine solution in the two-phase system of benzene–xylene and water in a stirred reactor with sodium hydroxide as an acid scavenger.
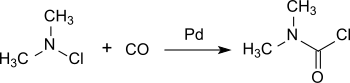
[5] A more recent process is based on chlorodimethylamine, which is converted practically quantitatively to dimethylcarbamoyl chloride on a palladium catalyst under pressure with carbon monoxide at room temperature.
[9] Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride is a clear, colorless, corrosive and flammable liquid with a pungent odor and a tear-penetrating effect, which decomposes rapidly in water.
Therefore, it reacts with alcohols, phenols and oximes to the corresponding N,N-dimethylcarbamates, with thiols to thiolourethanes, with amines and hydroxylamines to substituted ureas, and with imidazoles and triazoles to carbamoylazoles.
[18] DMCC is a starting material for the insecticide class of the dimethyl carbamates which act as inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase, including dimetilane,[19] and the related compounds isolane, pirimicarb and triazamate.