Tris(dimethylamino)methane
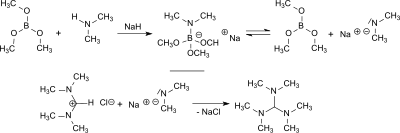
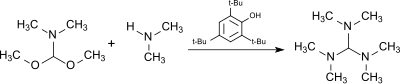
[6] The reaction of the dimethylformamide (DMF) dimethylacetal, HC(OCH3)2N(CH3)2, (from the DMF–dimethyl sulfate complex and sodium methoxide[7]) with dimethylamine in the presence of the acidic catalyst 2,4,6-tri-tert-butylphenol (which is largely stable to the alkylating agent) produces tris(dimethylamino)methane.
[6] Tris(dimethylamino)methane is a clear, colorless or pale yellow liquid with a strong ammoniacal odor.
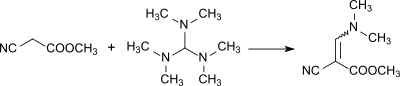
However, when heated tris(dimethylamino)methane reacts with protic solvents (such as water or alcohols) but also with weak CH-acidic substances, such as acetone or acetonitrile.
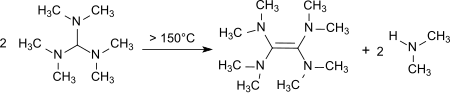
[2] Upon heating to 150–190 °C decomposition occurs with the formation of tetrakis(dimethylamino)ethene,[12] a strong electron donor.
[13] Tris(dimethylamino)methane dissociates into N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylformamidinium cations and dimethylamide anions, which abstract protons from CH- and NH-acidic compounds.