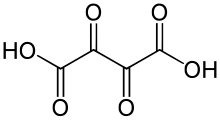
Dioxosuccinic acid
Removal of two protons from the molecule would yield the dioxosuccinate anion, C4O2−6 or −O−(C=O)4−O−.
This is one of the oxocarbon anions, which consist solely of carbon and oxygen.
Removal of a single proton would result in the monovalent anion hydrogendioxosuccinate, C4HO−6 or HO−(C=O)4−O−.
Indeed, the product traded under the name "dioxosuccinic acid hydrate" appears to be that substance.
[citation needed] Dihydroxytartaric acid behaves like dioxosuccinic acid in some reactions; for example, it reacts with ethanol in the presence of hydrogen chloride to yield the ester diethyl dioxosuccinate, upon isolation.