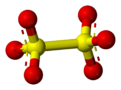
Dithionate
The sulfur atoms of the dithionate ion are in the +5 oxidation state due to the presence of the S–S bond.
Generally, dithionates form stable compounds that are not readily oxidised or reduced.
[4] Aqueous solutions of dithionates are quite stable and can be boiled without decomposition.
[5] The γ-irradiation of crystalline dithionates produces SO•−3 radical ions.
[8] The structure of the dithionate ion in the solid state is staggered in Na2S2O6·2H2O, whereas in the anhydrous potassium salt it is nearly eclipsed.