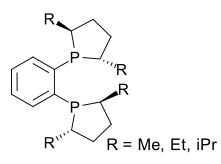
DuPhos
Both compounds can be obtained from the corresponding chiral diol through conversion to the cyclic sulfate and reaction with lithiated phenylbisphosphine.
In DuPhos the phosphorus atoms are electron-rich making the resulting metal complexes reactive.
The phosphorus atoms also introduce a kind of pseudo-chirality making enantioselection independent of the overall chemical conformation[5] Another early application is the synthesis of unnatural chiral amino acids in a formal reductive amination[6] for example starting from benzophenone and the hydrazone of benzoyl chloride:[7] In the original scope the metal catalyst was rhodium but catalysis by ruthenium was introduced in 1995 [8] with the hydrogenation of the ketone group in β-keto esters: An application of an asymmetric synthesis with a DuPhos ligand is the hydrogenation of dehydrowarfarin to warfarin:[9] Duphos is also applied in the synthesis of tryptophan derivatives.
[10] DuPhos ligands are used in metal catalyzed alpha-olefin/carbon monoxide copolymerization to form chiral isotactic polyketones.
The first publication in this field dates back to 1994 with catalyst system [Pd(Me-DuPhos(MeCN)2)](BF4)2[11] Mono oxidation of (R,R)-Me-Duphos using borane dimethylsulfide as protective group and hydrogen peroxide as oxidizing agent gives bozPhos [12][13] This ligand is useful in copper-catalyzed asymmetric addition of diorganozinc reagents to N-diphenylphosphinoylimines.