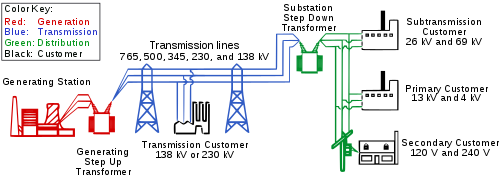
Electric power transmission
A wide area synchronous grid, known as an interconnection in North America, directly connects generators delivering AC power with the same relative frequency to many consumers.
If demand exceeds supply, the imbalance can cause generation plant(s) and transmission equipment to automatically disconnect or shut down to prevent damage.
Wind speeds as low as 23 knots (43 km/h) can permit conductors to encroach operating clearances, resulting in a flashover and loss of supply.
In some metropolitan areas, cables are enclosed by metal pipe and insulated with dielectric fluid (usually an oil) that is either static or circulated via pumps.
[9] Transmission of alternating current (AC) became possible after Lucien Gaulard and John Dixon Gibbs built what they called the secondary generator, an early transformer provided with 1:1 turn ratio and open magnetic circuit, in 1881.
It was powered by a 2 kV, 130 Hz Siemens & Halske alternator and featured several Gaulard transformers with primary windings connected in series, which fed incandescent lamps.
[10] Working to improve what he considered an impractical Gaulard-Gibbs design, electrical engineer William Stanley, Jr. developed the first practical series AC transformer in 1885.
[16] Alternating current's economies of scale with large generating plants and long-distance transmission slowly added the ability to link all the loads.
The first transmission of single-phase alternating current using high voltage came in Oregon in 1890 when power was delivered from a hydroelectric plant at Willamette Falls to the city of Portland 14 miles (23 km) down river.
At times of lower interest rates and low commodity costs, Kelvin's law indicates that thicker wires are optimal.
High-voltage direct current (HVDC) systems require relatively costly conversion equipment that may be economically justified for particular projects such as submarine cables and longer distance high capacity point-to-point transmission.
The slowly varying portion of demand is known as the base load and is generally served by large facilities with constant operating costs, termed firm power.
Hydro and wind sources cannot be moved closer to big cities, and solar costs are lowest in remote areas where local power needs are nominal.
Transmitting electricity at high voltage reduces the fraction of energy lost to Joule heating, which varies by conductor type, the current, and the transmission distance.
High-voltage direct current (HVDC) is used to transmit large amounts of power over long distances or for interconnections between asynchronous grids.
When electrical energy is transmitted over very long distances, the power lost in AC transmission becomes appreciable and it is less expensive to use direct current instead.
[33] A 2024 report found the United States behind countries like Belgium and the Netherlands in adoption of this technique to accommodate electrification and renewable energy.
[34] In April 2022, the Biden Administration streamlined environmental reviews for such projects, and in May 2022 announced competitive grants for them funded by the 2021 Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and 2022 Inflation Reduction Act.
Replacing the steel with a lighter, stronger composite material such as carbon fiber (ACCC conductor) allows lines to operate at higher temperatures, with less sag, and doubled transmission capacity.
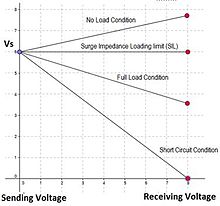
The voltage, power, frequency, load factor, and reliability capabilities of the transmission system are designed to provide cost effective performance.
The main draw of locally distributed generation systems is that they reduce transmission losses by leading to consumption of electricity closer to where it was produced.
Fault-sensing protective relays at each end of the line must communicate to monitor the flow of power so that faulted conductors or equipment can be quickly de-energized and the balance of the system restored.
Some jurisdictions, such as Minnesota, prohibit energy transmission companies from selling surplus communication bandwidth or acting as a telecommunications common carrier.
[42] A major barrier to wider adoption of merchant transmission is the difficulty in identifying who benefits from the facility so that the beneficiaries pay the toll.
[43] In the United States, the FERC's Order 1000, issued in 2010, attempted to reduce barriers to third party investment and creation of merchant transmission lines where a public policy need is found.
[46] Mainstream scientific evidence suggests that low-power, low-frequency, electromagnetic radiation associated with household currents and high transmission power lines does not constitute a short- or long-term health hazard.
The development of superconductors with transition temperatures higher than the boiling point of liquid nitrogen has made the concept of superconducting power lines commercially feasible, at least for high-load applications.
[55] It has been estimated that waste would be halved using this method, since the necessary refrigeration equipment would consume about half the power saved by the elimination of resistive losses.
Both Nikola Tesla and Hidetsugu Yagi attempted to devise systems for large scale wireless power transmission in the late 1800s and early 1900s, without commercial success.
[66] The New York Times reported that American hackers from the United States Cyber Command planted malware potentially capable of disrupting the Russian electrical grid.