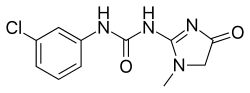
Fenobam
Fenobam is an imidazole derivative developed by McNeil Laboratories in the late 1970s as a novel anxiolytic drug with an at-the-time-unidentified molecular target in the brain.
Subsequently, it was determined that fenobam acts as a potent and selective negative allosteric modulator of the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5,[1][2] and it has been used as a lead compound for the development of a range of newer mGluR5 antagonists.
[9][10] Following the discovery of its activity as a potent negative allosteric modulator of mGluR5, fenobam has been re-investigated for many applications, with its profile of combined antidepressant, anxiolytic, analgesic and anti-addictive effects potentially useful given the common co-morbidity of these symptoms.
[11][12] It has also shown promising initial results in the treatment of fragile X syndrome.
[14] Fenobam is known to exist in five crystalline forms, all of them exhibiting a tautomeric structure with the proton attached to the five membered ring nitrogen.