Fertility testing
The onset of puberty is typically identified by menarche and the presence of secondary sexual characteristics such as breast development, the appearance of pubic hair and changes to body fat distribution.
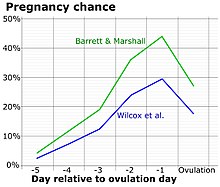
Knowing the timing of ovulation can help a woman to determine the days of the menstrual cycle that are most likely to result in conception.
A fertility monitor may analyze changes in hormone levels in urine, basal body temperature, electrical resistance of saliva and vaginal fluids, or a combination of these methods.
Higher levels of progesterone released during the menstrual cycle causes an abrupt increase in basal body temperature by 0.5 °C to 1 °C at the time of ovulation.
Some use a combination of imaging such as an X-ray or ultrasound with a contrast agent to visualize anatomic structures within the uterus and fallopian tubes.
AMH testing is considered to be one of the most accurate estimates of ovarian reserve, can be used for assessment at any point in the menstrual cycle, and is non-invasive.
To test for ovarian reserve in women with infertility, FSH levels are measured from blood samples taken on day three of the menstrual cycle and compared to standards to determine the likelihood of pregnancy after IVF treatment.
A physician may use a transvaginal ultrasound to visualize and count the number of antral follicles in each of a woman's ovaries in order to determine her ovarian reserve; however AFC is not predictive of embryo quality.
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) is an invasive x-ray imaging technique used to evaluate the shape and size of the uterus and openness of the fallopian tubes.
[16][17] Risks associated with HSG are rare and include exposure to radiation, infection, allergic reactions to the contrast dye or antiseptic.
It is normal for patients to experience mild to moderate abdominal cramping, pain and vaginal spotting for a few days after the procedure.
[16] Hystero contrast sonography (HyCoSy) is a transvaginal ultrasound imaging technique used to evaluate the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries.
The cervix is cleaned with an antiseptic such as iodine and injected with a local anesthetic to minimize discomfort and pain.
A small catheter is used to fill the uterus and fallopian tubes with a contrast agent consisting of a galactose solution called Echovist to enhance visibility.
A transvaginal ultrasound is inserted into the vagina and manually positioned to visualize the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
[18]An alternative to saline and Echovist, the galactose solution used to enhance visualization of anatomic features via ultrasound in HyCoSy, was needed because of limitations and high costs.
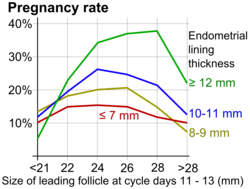
[18] Ultrasound scans of the ovaries (optimally by transvaginal ultrasonography) may be conducted to establish the development of ovarian follicles.
Hysteroscopy is used to visualize the inside of the uterus using a thin, lighted, flexible camera that is inserted vaginally and through the cervix.
Laparoscopy is a minimally-invasive surgical procedure in which a camera is inserted into the abdominal cavity via a small (0.5 - 1.5 cm) incision.
Though considered to be a "gold standard" for diagnosing disorders of fallopian tube patency, it is an invasive procedure requiring general anesthesia.
After intercourse, sperm travel to the egg through the female reproductive tract, typically causing fertilisation to occur in the fallopian tubes.
Checks are also made to identify undescended testicles and retrograde ejaculation, along with medical history, such as cancer treatment, radiation, drug use, etc.