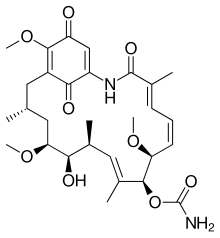
Geldanamycin
[2] Geldanamycin induces the degradation of proteins that are mutated or overexpressed in tumor cells such as v-Src, Bcr-Abl, p53, and ERBB2.
Despite its potent antitumor potential, geldanamycin presents several major drawbacks as a drug candidate such as hepatotoxicity, further, Jilani et al.. reported that geldanamycin induces the apoptosis of erythrocytes under physiological concentrations.
The genes gelA, gelB, and gelC encode for the polyketide synthase.
It then utilizes malonyl-CoA, methylmalonyl-CoA, and methoxymalonyl-CoA to synthesize the precursor molecule Progeldanamycin.
[6] This precursor is subjected to several enzymatic and non-enzymatic tailoring steps to produce the active molecule geldanamycin, which include hydroxylation, O-methylation, carbamoylation, and oxidation.