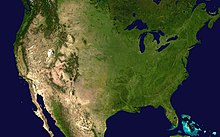
Geography of the United States
By total area (water as well as land), the United States is either slightly larger or smaller than the People's Republic of China, making it the world's third or fourth-largest country.
By land area only (exclusive of waters), the United States is the world's third largest country, after Russia and China, with Canada in fourth.
Since the initial publishing of the World Factbook, the CIA has updated the total area of the United States several times.
A broad, flat coastal plain lines the Atlantic and Gulf shores from the Texas-Mexico border to New York City, and includes the Florida peninsula.
This broad coastal plain and barrier islands make up the widest and longest beaches in the United States, much of it composed of soft, white sands.
Areas further inland feature rolling hills, mountains, and a diverse collection of temperate and subtropical moist and wet forests.
It is located at the boundary between California's Inyo and Tulare counties, just 84.6 mi or 136.2 km west-northwest of the lowest point in North America at the Badwater Basin in Death Valley National Park at 279 ft or 85 m below sea level.
Hawaii, far to the south of Alaska in the Pacific Ocean, is a chain of tropical, volcanic islands, popular as a tourist destination for many from East Asia and the mainland United States.
The territories of Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands encompass a number of tropical isles in the northeastern Caribbean Sea.
In the Pacific Ocean the territories of Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands occupy the limestone and volcanic isles of the Mariana archipelago, and American Samoa (the only populated US territory in the southern hemisphere) encompasses volcanic peaks and coral atolls in the eastern part of the Samoan Islands chain.
This system had its climax of deformation so long ago (probably in Permian time) that it has since then been very generally reduced to moderate or low relief.
The oblique trend of this coast would be even more pronounced but for a comparatively modern crustal movement, causing a depression in the northeast resulting in an encroachment of the sea upon the land.
The east coast Appalachian system, originally forest covered, is relatively low and narrow and is bordered on the southeast and south by an important coastal plain.
The uplands towards the Appalachians were included in the great eastern forested area, while the western part of the plains has an arid climate supporting only scanty native plant life, and in the south, it is practically barren.
Elevation extremes: Due to its large size and wide range of geographic features, the United States contains examples of nearly every global climate.
The Cascade Range, Sierra Nevada, and Rocky Mountains pick up most of the moisture from these systems as they move eastward via the orographic effect, and they are greatly diminished by the time they reach the High Plains.
Temperatures can rise or drop rapidly, winds can be extreme, and the flow of heat waves or Arctic air masses often advance uninterrupted through the plains.
The Great Basin and Columbia Plateau (the Intermontane Plateaus) are arid or semiarid regions that lie in the rain shadow of the Cascades and Sierra Nevada.
The Southwest and the Great Basin are also affected by the monsoon from the Gulf of California from July to September, which brings localized but often severe thunderstorms to the region.
The mild winters of Florida allow a massive tropical fruit industry to thrive in the central part of the state, making the US second to only Brazil in citrus production worldwide.
Another significant (but localized) weather effect is lake-effect snow that falls south and east of the Great Lakes, especially in the hilly portions of the Upper Peninsula of Michigan and on the Tug Hill Plateau in New York.
Along the northwestern Pacific coast, rainfall is greater than anywhere else in the continental U.S., with Quinault Rainforest in Washington having an average of 137 inches (348 cm).
[17] The Mojave Desert, in the southwest, is home to the driest locale in the U.S. Yuma, Arizona, has an average of 2.63 inches (6.7 cm) of precipitation each year.
However, the remnants of tropical cyclones from the Eastern Pacific occasionally impact the western United States, bringing moderate to heavy rainfall.
The West Coast of the continental United States makes up part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, an area of heavy tectonic and volcanic activity that is the source of 90% of the world's earthquakes.
[28] The American Northwest sees the highest concentration of active volcanoes in the United States, in Washington, Oregon and northern California along the Cascade Mountains.
California is well known for seismic activity and requires large structures to be earthquake resistant to minimize loss of life and property.
[30] Other natural disasters include tsunamis around the Pacific Basin, mudslides in California, and forest fires in the western half of the contiguous U.S.
The survey-report stated that in Florida, the devastation caused by Hurricanes Ian and Nicole resulted in the relocation of around 1 million people, or about one in every 17 adult residents.
For lists of areas, see the following articles: In terms of human geography, the United States is inhabited by a diverse set of ethnicities and cultures.