Histone acetylation and deacetylation
As a consequence, the condensed chromatin is transformed into a more relaxed structure that is associated with greater levels of gene transcription.
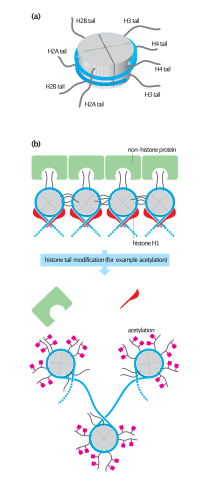
[1] Nucleosomes are portions of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) that are wrapped around protein complexes called histone cores.
Nucleosomes are formed as a beginning step for DNA compaction that also contributes to structural support as well as serves functional roles.
The histone tails insert themselves in the minor grooves of the DNA and extend through the double helix,[1] which leaves them open for modifications involved in transcriptional activation.
When a lysine is to be deacetylated, factors known as histone deacetylases (HDACs) catalyze the removal of the acetyl group with a molecule of H2O.
[5][6][7] Acetylated histones, the octomeric protein cores of nucleosomes, represent a type of epigenetic marker within chromatin.
[10][11] Major features of the GNAT family include HAT domains approximately 160 residues in length and a conserved bromodomain that has been found to be an acetyl-lysine targeting motif.
The members of this family have multiple functions, not only with activating and silencing genes, but also affect development and have implications in human diseases.
[5] These enzymes have been found to be inactive when isolated which led to the conclusion that they must be incorporated with cofactors in order to activate their deacetylase abilities.
Northern blots have revealed that different tissue types show varying degrees of HDAC8 expression[5] but has been observed in smooth muscles and is thought to contribute to contractility.
[5][6] Another unique feature of HDAC6 is the HDAC6-, SP3, and Brap2-related zinc finger motif (HUB) domain in the C-terminus which shows some functions related to ubiquitination, meaning this HDAC is prone to degradation.
[5] The discovery of histone acetylation causing changes in transcription activity can be traced back to the work of Vicent Allfrey and colleagues in 1964.
[15] Histone modification is now considered a major regulatory mechanism that is involved in many different stages of genetic functions.
The acetyl group is removed by one of the HDAC enzymes during deacetylation, allowing histones to interact with DNA more tightly to form compacted nucleosome assembly.
It has been hypothesized that the histone tails offer recognition sites that attract proteins responsible for transcriptional activation.
This specific addition of single or multiple modifications on histone cores can be interpreted by transcription factors and complexes which leads to functional implications.
For example, the combination of acetylation and phosphorylation have synergistic effects on the chromosomes overall structural condensation level and, hence, induces transcription activation of immediate early gene.
[8] The acetylation pattern is regulated by HAT and HADC enzymes and, in turn, sets the local chromatin structure.
[23] Structural analysis of transcription factors has shown that highly conserved bromodomains are essential for protein to bind to acetylated lysine.
[27] Results have shown that there is an important role for HAT/HDAC activity balance in inflammatory lung diseases and provided insights on possible therapeutic targets.
The overexpression and increased activity of HDACs has been shown to be characteristic of tumorigenesis and metastasis, suggesting an important regulatory role of histone deacetylation on the expression of tumor suppressor genes.
Vorinostat targets histone acetylation mechanisms and can effectively inhibit abnormal chromatin remodeling in cancerous cells.
PDC and ACLY activity depend on glucose availability, which thereby influences histone acetylation and consequently modulates gene expression and cell cycle progression.
SIRT enzyme activity is altered in various malignancies, and inhibiting SIRT6, a histone deacetylase that acts on acetylated H3K9 and H3K56, promotes tumorigenesis.
SIRT7, which deacetylates H3K18 and thereby represses transcription of target genes, is activated in cancer to stabilize cells in the transformed state.
In the nucleus accumbens of the brain, Delta FosB functions as a "sustained molecular switch" and "master control protein" in the development of an addiction.
In rats exposed to alcohol for up to 5 days, there was an increase in histone 3 lysine 9 acetylation in the pronociceptin promoter in the brain amygdala complex.
[44][45] At least 45 genes, shown in previous studies to be upregulated in the NAc of mice after chronic cocaine exposure, were found to be associated with hyperacetylation of H3 or H4.
[38] Suggested by the idea that the structure of chromatin can be modified to allow or deny access of transcription activators, regulatory functions of histone acetylation and deacetylation can have implications with genes that cause other diseases.
[60] Current studies indicate that inhibitors of the HDAC family have therapeutic benefits in a wide range of neurological and psychiatric disorders.