History of the United States
Dissatisfaction with corruption, inefficiency, and traditional politics stimulated the Progressive movement, leading to reforms including the federal income tax, direct election of Senators, citizenship for many Indigenous people, alcohol prohibition, and women's suffrage.
[1] Following the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, the United States entered World War II, helping defeat Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy in the European theater.
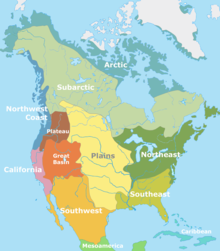
The prevailing theory proposes that people from Eurasia followed game across Beringia, a land bridge that connected Siberia to present-day Alaska during the Ice Age, and then spread southward, perhaps as early as 30,000 years ago.
Originally, Paleo-Indians hunted Ice Age megafauna like mammoths, but as they began to go extinct, people turned instead to bison as a food source, and later foraging for berries and seeds.
Cahokia, like many other cities and villages of the time, depended on hunting, foraging, trading, and agriculture, and developed a class system with slaves and human sacrifice that was influenced by societies to the south, like the Mayans.
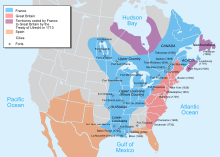
[21][22] Spanish explorers were the first Europeans, after the Norse, to reach the present-day United States, after the voyages of Christopher Columbus (beginning in 1492) established possessions in the Caribbean, including the modern-day U.S. territories of Puerto Rico, and parts of the U.S. Virgin Islands.
Roger Williams opposed Winthrop's treatment of Native Americans and religious intolerance, and established the colony of Providence Plantations, later Rhode Island, on the basis of freedom of religion.
Typically, a colony was ruled by a governor appointed from London who controlled the executive administration and relied upon a locally elected legislature to vote on taxes and make laws.
[35] Typically, people would sign a contract agreeing to a set term of labor, usually four to seven years, and in return would receive transport to America and a piece of land at the end of their servitude.
[36] Initially regarded as indentured servants who could buy their freedom, the institution of slavery began to harden and the involuntary servitude became lifelong[36] as the demand for labor on tobacco and rice plantations grew in the 1660s.
Parliament responded the next year with the Intolerable Acts, stripping Massachusetts of its historic right of self-government and putting it under military rule, which sparked outrage and resistance in all thirteen colonies.
To assuage the Anti-Federalists who feared a too-powerful central government, the Congress adopted the United States Bill of Rights in 1791, which guaranteed individual liberties such as freedom of speech and religious practice.
War loomed with France and the Federalists used the opportunity to try to silence the Republicans with the Alien and Sedition Acts, build up a large army with Hamilton at the head, and prepare for a French invasion.
In 1864, Union General William Tecumseh Sherman marched south from Chattanooga to capture Atlanta, a decisive victory that ended war jitters among Republicans in the North and helped Lincoln win re-election.
[140][141] The "Gilded Age" was a term that Mark Twain used to describe the period of the late 19th century with a dramatic expansion of American wealth and prosperity, underscored by mass corruption in government.
[143][144][145] As financiers and industrialists such as J.P. Morgan and John D. Rockefeller began to amass vast fortunes, many observers were concerned that the nation was losing its pioneering egalitarian spirit.
[148][149][150] Dissatisfaction on the part of the growing middle class with the corruption and inefficiency of politics, and the failure to deal with increasingly important urban and industrial problems, led to the dynamic progressive movement starting in the 1890s.
Four new constitutional amendments – the Sixteenth through Nineteenth – resulted from progressive activism, bringing the federal income tax, direct election of Senators, prohibition, and female suffrage.
U.S. legislation in the Neutrality Acts sought to avoid foreign conflicts; however, policy clashed with increasing anti-Nazi feelings following the German invasion of Poland in September 1939 that started World War II.
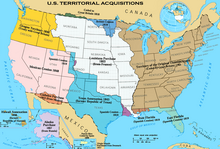
[212] The Truman Doctrine in 1947 was the U.S.' attempt to secure trading partners in Europe, by providing military and economic aid to Greece and Turkey to counteract the threat of communist expansion in the Balkans.
[213][208] In 1948, the United States replaced piecemeal financial aid programs with a comprehensive Marshall Plan, which pumped money into Western Europe, and removed trade barriers, while modernizing the managerial practices of businesses and governments.
State laws criminalized spousal abuse and marital rape, and the Supreme Court ruled that the equal protection clause of the Fourteenth Amendment applied to women.
Abortion, deemed by the Supreme Court as a fundamental right in Roe v. Wade (1973), is still a point of debate.President Richard Nixon (1969–1974) largely continued the New Deal and Great Society programs he inherited.
The Watergate scandal, involving Nixon's cover-up of his operatives' break-in into the Democratic National Committee headquarters, destroyed his political base and forced his resignation on August 9, 1974.
In South America, they supported Argentina and Chile, who carried out Operation Condor, a campaign of assassinations of exiled political opponents by Southern Cone governments, created at the behest of Chilean dictator Augusto Pinochet in 1975.
[242][243][244] The OPEC oil embargo marked a long-term economic transition: energy prices skyrocketed, and American factories faced serious competition from foreign automobiles, clothing, electronics, and consumer goods.
The Soviets reacted harshly because they thought it violated the 1972 Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty, and would give the U.S. a major military advantage, so they stopped negotiating disarmament deals until the late 1980s.
Every building of the World Trade Center partially or completely collapsed, massively damaging the surrounding area and blanketing Lower Manhattan in toxic dust clouds.
[352][353][354] He confirmed three new Supreme Court justices (cementing a conservative majority),[355] started a trade war with China,[356] signed the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, and removed the U.S. from the Paris Agreement.
[424] In 2022, the Supreme Court ruled in Dobbs v. Jackson that having an abortion is not a protected Constitutional right, overturning Roe v. Wade and Planned Parenthood v. Casey and sparking nationwide protests.