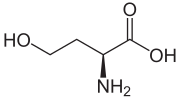
Homoserine
Homoserine (also called isothreonine) is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH(NH2)CH2CH2OH.
It differs from the proteinogenic amino acid serine by insertion of an additional -CH2- unit into the backbone.
Homoserine, or its lactone form, is the product of a cyanogen bromide cleavage of a peptide by degradation of methionine.
[2] Specifically, the enzyme homoserine dehydrogenase, in association with NADPH, catalyzes a reversible reaction that interconverts L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde to L-homoserine.
[6] Bacterial cell lines can make copious amounts of this amino acid.