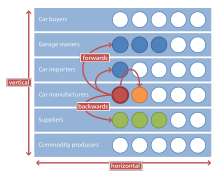
Horizontal integration
Horizontal integration is the process of a company increasing production of goods or services at the same level of the value chain, in the same industry.
[3] Benefits of horizontal integration include: increasing economies of scale, expanding an existing market, and improving product differentiation.
[9] M&A activities can be an effective way for companies to expand their operations, diversify their product or service offerings, and increase their market share.
This can occur through a stock-for-stock transaction, where shareholders of both companies receive shares in the new entity based on a predetermined exchange ratio.
Shareholders can benefit from increased stock prices and dividends, while employees may face job losses or changes to their employment terms.
[17] Regulatory bodies play an important role in overseeing M&A activities to ensure they do not violate antitrust laws and do not harm competition in the marketplace.
However, careful consideration of the potential benefits and drawbacks, as well as regulatory compliance, is essential to ensure a successful outcome for all stakeholders involved.
[21] This strategy can enable companies to increase their market share and achieve economies of scale by leveraging existing resources and capabilities.
[26] Overall, internal expansion through horizontal integration can be a viable strategy for companies looking to achieve growth and gain a competitive advantage.
[citation needed] That emerged are new strategies for content development and distribution designed to increase the "synergy" between the different divisions of the same company.
On 9 December 2013, Sysco agreed to acquire US Foods but on 24 June 2015, the federal judge ruled against the deal saying that such merger would control 75% of the U.S. foodservice industry and that will stifle competition.
On 16 November 2015, Marriott International announced that it would acquire Starwood for $13.6 billion, creating the world's largest hotel chain.