Isoline retrieval
When used to retrieve a whole field, it is a general, nonlinear inverse method and a robust estimator.
Since satellite instruments cannot measure the constituent directly, we need to perform some sort of inversion.
, which we approximate by collecting samples, called training data, of both the measurement vector and the state variable, q.
By generating classification results over the region of interest and using any contouring algorithm to separate the two classes, the isoline will have been "retrieved."
We can maximize this quantity by maximizing the value of the integrand at each point: Since this is the definition of maximum likelihood, a classification algorithm based on maximum likelihood is the most accurate method possible of validating an advected contour.
A good method for performing maximum likelihood classification from a set of training data is variable kernel density estimation.
In this case, no knowledge of the actual physics that produce the measurement is required and the retrieval algorithm is purely statistical.
Since retrievals will be biased towards more common states, however, the statistics ought to reflect those in the real world.
, provide excellent error characterization, therefore the classification algorithm ought to return them.
We define the confidence rating by rescaling the conditional probability: where nc is the number of classes (in this case, two).
The function relates the threshold value of the confidence rating for which the tolerance is applicable.
That is, it defines a region that contains a fraction of the true isoline equal to the tolerance.
The Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit (AMSU) series of satellite instruments are designed to detect temperature and water vapour.
They have a high horizontal resolution (as little as 15 km) and because they are mounted on more than one satellite, full global coverage can be obtained in less than one day.
Thus we expect the true isoline to fall within the shading 90 percent of the time.
It has the advantage over both a neural network, as well as iterative methods such as optimal estimation that invert the forward model directly, in that there is no possibility of getting stuck in a local minimum.
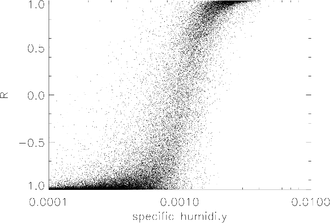
is the standard deviation, then the conditional probability is related to the continuum variable, q, by the error function: The figure shows conditional probability versus specific humidity for the example retrieval discussed above.