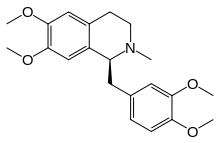
Laudanosine
Laudanosine or N-methyltetrahydropapaverine is a recognized metabolite[1] of atracurium and cisatracurium.
Laudanosine decreases the seizure threshold, and thus it can induce seizures if present at sufficient threshold concentrations; however such concentrations are unlikely to be produced consequent to chemodegradable metabolism of clinically administered doses of cisatracurium or atracurium.
Laudanosine also occurs naturally in minute amounts (0.1%) in opium, from which it was first isolated in 1871.
[2] Partial dehydrogenation of laudanosine will lead to papaverine, the alkaloid found in the opium poppy plant (Papaver somniferum).
This drug article relating to the nervous system is a stub.