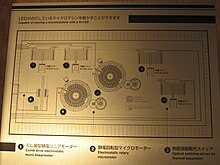
Micromachinery
Micromachines are mechanical objects that are fabricated in the same general manner as integrated circuits.
The applications of micromachines include accelerometers that detect when a car has hit an object and trigger an airbag.
This technique is termed an etchstop as the doping of boron produces an unetchable layer/pattern.
The increased mass alters the resonance frequency of the mechanical object, which is detected with circuitry.
Two mechanical elements, one that is stationary (the stator) and one that is movable (the rotor) have two different voltages applied to them, which creates an electric field.