Coronary artery disease
[10][23] In those with stable CAD it is unclear if PCI or CABG in addition to the other treatments improves life expectancy or decreases heart attack risk.
[27] The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort that occurs regularly with activity, after eating, or at other predictable times; this phenomenon is termed stable angina and is associated with narrowing of the arteries of the heart.
[29] Angina, shortness of breath, sweating, nausea or vomiting, and lightheadedness are signs of a heart attack or myocardial infarction, and immediate emergency medical services are crucial.
These risk factors for CAD include "smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure (hypertension), abnormal (high) amounts of cholesterol and other fat in the blood (dyslipidemia), type 2 diabetes and being overweight or obese (having excess body fat)" due to lack of exercise and a poor diet.
[40] In one study, females who were free of stress from work life saw an increase in the diameter of their blood vessels, leading to decreased progression of atherosclerosis.
[48] In contrast, females who had high levels of work-related stress experienced a decrease in the diameter of their blood vessels and significantly increased disease progression.
[52] The linear configurations of unsaturated trans and saturated fats allow them to easily accumulate and stack at the arterial walls when consumed in high amounts (and other positive measures towards physical health are not met).
[56] One of the most differentially expressed genes, fibromodulin (FMOD), which is increased 2.8-fold in CAD, is found mainly in connective tissue[57] and is a modulator of the TGF-beta signaling pathway.
For example, Nebulette, the most down-regulated transcript (2.4-fold), is found in cardiac muscle; it is a 'cytolinker' that connects actin and desmin to facilitate cytoskeletal function and vesicular movement.
The endocytic pathway is further modulated by changes in tubulin, a key microtubule protein, and fidgetin, a tubulin-severing enzyme that is a marker for cardiovascular risk identified by genome-wide association study.
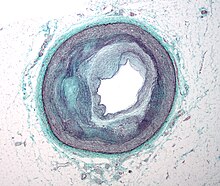
With atherosclerosis, the artery's lining becomes hardened, stiffened, and accumulates deposits of calcium, fatty lipids, and abnormal inflammatory cells – to form a plaque.
Calcium phosphate (hydroxyapatite) deposits in the muscular layer of the blood vessels appear to play a significant role in stiffening the arteries and inducing the early phase of coronary arteriosclerosis.
[citation needed] Although these people have kidney dysfunction, almost fifty percent of them die due to coronary artery disease.
[80] When nitroglycerine enters the bloodstream, it forms free radical nitric oxide, or NO, which activates guanylate cyclase and in turn stimulates the release of cyclic GMP.
This molecular signaling stimulates smooth muscle relaxation, resulting in vasodilation and consequently improved blood flow to heart regions affected by atherosclerotic plaque.
[85] Diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome generally takes place in the emergency department, where ECGs may be performed sequentially to identify "evolving changes" (indicating ongoing damage to the heart muscle).
Diagnosis is clear-cut if ECGs show elevation of the "ST segment", which in the context of severe typical chest pain is strongly indicative of an acute myocardial infarction (MI); this is termed a STEMI (ST-elevation MI) and is treated as an emergency with either urgent coronary angiography and percutaneous coronary intervention (angioplasty with or without stent insertion) or with thrombolysis ("clot buster" medication), whichever is available.
This process usually necessitates hospital admission and close observation on a coronary care unit for possible complications (such as cardiac arrhythmias – irregularities in the heart rate).
Depending on the risk assessment, stress testing or angiography may be used to identify and treat coronary artery disease in patients who have had an NSTEMI or unstable angina.
[94] A 2024 study published in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology found that the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is more effective than hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) for detecting dysglycemia in patients with coronary artery disease.
[102][103] The consumption of trans fat (commonly found in hydrogenated products such as margarine) has been shown to cause a precursor to atherosclerosis[104] and increase the risk of coronary artery disease.
[105] Evidence does not support a beneficial role for omega-3 fatty acid supplementation in preventing cardiovascular disease (including myocardial infarction and sudden cardiac death).
Effective lifestyle changes include: Aerobic exercise, like walking, jogging, or swimming, can reduce the risk of mortality from coronary artery disease.
[115] However, a 2021 Cochrane meta-analysis found that antibiotics given for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease are harmful to people with increased mortality and occurrence of stroke.
[117] There are a number of treatment options for coronary artery disease:[118] It is recommended that blood pressure typically be reduced to less than 140/90 mmHg.
[132] Hybrid coronary revascularization has also been shown to be a safe and feasible procedure that may offer some advantages over conventional CABG though it is more expensive.
[141] After analysing data from 2 111 882 patients, the recent meta-analysis revealed that the incidence of coronary artery diseases in breast cancer survivors was 4.29 (95% CI 3.09–5.94) per 1000 person-years.
The Infarct Combat Project (ICP) is an international nonprofit organization founded in 1998 which tries to decrease ischemic heart diseases through education and research.
[153] Treatment with antibiotics in patients with proven atherosclerosis has not demonstrated a decreased risk of heart attacks or other coronary vascular diseases.
[155] Plant-based nutrition has been suggested as a way to reverse coronary artery disease,[156] but strong evidence is still lacking for claims of potential benefits.