Natural product
For instance, alkaloids like morphine and nicotine act as defense chemicals against herbivores, while flavonoids attract pollinators, and terpenes such as menthol serve to repel insects.
Vitamin B3 (nicotinic acid or niacin), synthesized from tryptophan, is an essential part of the coenzymes NAD+ and NADP+, necessary for electron transport in the Krebs cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, and other redox processes.
[39] The shikimate pathway is a key metabolic route responsible for the production of aromatic amino acids and their derivatives in plants, fungi, bacteria, and some protozoans:[25]: Ch.
During translation, transfer RNA (tRNA) carries specific amino acids to match with mRNA codons, forming peptide bonds to create the protein chain.
Peptide hormones, such as oxytocin and vasopressin, are short amino acid chains that regulate physiological processes, including social bonding and water retention.
[65] The serendipitous discovery and subsequent clinical success of penicillin prompted a large-scale search for other environmental microorganisms that might produce anti-infective natural products.
Soil and water samples were collected from all over the world, leading to the discovery of streptomycin (derived from Streptomyces griseus), and the realization that bacteria, not just fungi, represent an important source of pharmacologically active natural products.
Examples of enzymes identified to date include amylases, pullulanases, cyclodextrin glycosyltransferases, cellulases, xylanases, chitinases, proteases, alcohol dehydrogenase, and esterases.
[80] Other medicinally useful fungal metabolites include lovastatin (from Pleurotus ostreatus), which became a lead for a series of drugs that lower cholesterol levels, cyclosporin (from Tolypocladium inflatum), which is used to suppress the immune response after organ transplant operations, and ergometrine (from Claviceps spp.
[88][89] As with plant feeding deterrents, this biological activity is attributed to natural selection, organisms capable of killing or paralyzing their prey and/or defending themselves against predators being more likely to survive and reproduce.
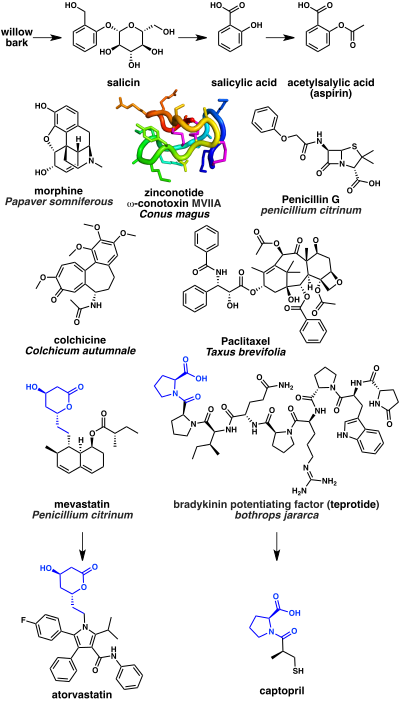
For example, teprotide, a peptide isolated from the venom of the Brazilian pit viper Bothrops jararaca, was a lead in the development of the antihypertensive agents cilazapril and captopril.
[94] Other natural products derived from marine animals and under investigation as possible therapies include the antitumour agents discodermolide (from the sponge Discodermia dissoluta),[95] eleutherobin (from the coral Erythropodium caribaeorum), and the bryostatins (from the bryozoan Bugula neritina).
[13] Additionally, natural products and their derivatives often show higher success rates in later clinical trial phases and may have lower toxicity profiles compared to synthetic compounds.
[105] The N-type calcium channel blocker ziconotide is an analgesic based on a cyclic peptide cone snail toxin (ω-conotoxin MVIIA) from the species Conus magus.
Penicillin and related beta lactams work by inhibiting the DD-transpeptidase enzyme that is required by bacteria to cross link peptidoglycan to form the cell wall.
[12][112] The biological resource for drug discovery from natural products remains abundant, with small percentages of microorganisms, plant species, and insects assessed for bioactivity.
[113][114] As of 2008, the field of metagenomics was proposed to examine genes and their function in soil microbes,[114][115] but most pharmaceutical firms have not exploited this resource fully, choosing instead to develop "diversity-oriented synthesis" from libraries of known drugs or natural sources for lead compounds with higher potential for bioactivity.
Determination of the absolute configuration often relies on a combination of NMR data (coupling constants and nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE), chemical derivatization methods (e.g., Mosher's ester analysis), and spectroscopic techniques like vibrational circular dichroism (VCD), and optical rotatory dispersion (ORD).
In cases where traditional methods are insufficient, especially for novel compounds with unprecedented molecular skeletons, advanced computational chemistry approaches are used to predict and compare spectral data, helping to elucidate the complete structure including stereochemistry.
In these cases, isolation from natural sources may be sufficient if it provides adequate quantities, as seen with drugs like penicillin, morphine, and paclitaxel, which were obtained at commercial scales without significant synthetic chemistry.
[129][130] Biomimetic synthesis is a branch of organic chemistry which aims at designing and preparing natural product compounds in the laboratory using the biosynthetic pathways as a blueprint.
[134] Biomimetic synthetic strategies have emerged due to their ability to simplify the synthesis of complex structures, especially those containing unusual moieties like spiro-ring systems or quaternary carbon atoms.
Density functional theory (DFT), the Hartree–Fock method, and semiempirical calculations also show some favorability for dimerization in natural products due to evolution of more energy per bond than the equivalent trimer or tetramer.
Isolating and identifying natural products has been important to source substances for early preclinical drug discovery research, to understand traditional medicine and ethnopharmacology, and to find pharmacologically useful areas of chemical space.
Early attempts to understand the biosynthesis of natural products, saw chemists employ first radiolabelling and more recently stable isotope labeling combined with NMR experiments.
[145] Lavoisier showed at the end of the 18th century that organic substances consisted of a limited number of elements: primarily carbon and hydrogen and supplemented by oxygen and nitrogen.
Initially, this idea faced skepticism, but it gained acceptance 20 years later when Adolph Wilhelm Hermann Kolbe synthesized acetic acid from carbon disulfide.
This issue became evident in a dispute between Friedrich Wöhler and Justus von Liebig, who studied silver salts with identical compositions but different properties.
[152][153] A definitive structure theory was proposed in 1858 by August Kekulé, who suggested that carbon is tetravalent and can bond to itself, forming chains found in natural products.
[154][153] The concept of natural product, which initially based on organic compounds that could be isolated from plants, was extended to include animal material in the middle of the 19th century by the German Justus von Liebig.