Nitrite
In valence bond theory, it is described as a resonance hybrid with equal contributions from two canonical forms that are mirror images of each other.
[2] Addition of acid to a solution of a nitrite in the presence of a reducing agent, such as iron(II), is a way to make nitric oxide (NO) in the laboratory.
Standard reduction potentials for reactions directly involving nitrous acid are shown in the table below:[4] The data can be extended to include products in lower oxidation states.
[5] Nitrite is an ambidentate ligand and can form a wide variety of coordination complexes by binding to metal ions in several ways.
[1] The addition of nitrites and nitrates to processed meats such as ham, bacon, and sausages reduces growth and toxin production of Clostridium botulinum.
[10] On the other hand, a 2018 study by the British Meat Producers Association determined that legally permitted levels of nitrite do not affect the growth of C.
[10] In mice, food rich in nitrites together with unsaturated fats can prevent hypertension by forming nitro fatty acids that inhibit soluble epoxide hydrolase, which is one explanation for the apparent health effect of the Mediterranean diet.
[17] 95% of the nitrite ingested in modern diets comes from bacterial conversion of nitrates naturally found in vegetables.
[19][20] Nitrite reacts with the meat's myoglobin by attaching to the heme iron atom, forming reddish-brown nitrosomyoglobin and the characteristic pink "fresh" color of nitrosohemochrome or nitrosyl-heme upon cooking.
According to scientists working for the industry group American Meat Institute, this use of nitrite started in the Middle Ages.
[22] Historians and epidemiologists argue that the widespread use of nitrite in meat-curing is closely linked to the development of industrial meat-processing.
[29] In organic chemistry, alkyl nitrites are esters of nitrous acid and contain the nitrosoxy functional group.
Nitrite salts can react with secondary amines to produce N-nitrosamines, which are suspected of causing stomach cancer.
[10][32] Nitrite (ingested) under conditions that result in endogenous nitrosation, specifically the production of nitrosamine, has been classified as Probably carcinogenic to humans (Group 2A) by the IARC.
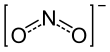


2 , which contribute to the resonance hybrid for the nitrite ion


