Non-price competition
[2] It is a form of competition that requires firms to focus on product differentiation instead of pricing strategies among competitors.
Such differentiation measures allowing for firms to distinguish themselves, and their products from competitors, may include, offering superb quality of service, extensive distribution, customer focus, or any sustainable competitive advantage other than price.
Non-price competition typically involves promotional expenditures (such as advertising, selling staff, the locations convenience, sales promotions, coupons, special orders, or free gifts), marketing research, new product development, and brand management costs.
Non-price competition is a key strategy in a growing number of marketplaces (oDesk, TaskRabbit, Fiverr, AirBnB, mechanical turk, etc) whose sellers offer their Service as a product, and where the price differences are virtually negligible when compared to other sellers of similar productized services on the same marketplaces.
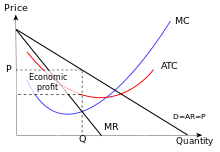
Due to having rather fixed market prices, leading to inelastic demand, they engage in product differentiation.
The more different the products of rival firms are, the lower the cross effects between their markets with regards to both non-price and price variables.
[6] By offering a wide range of products, firms can not only achieve economies of scope, but also be able to expand their market base.
There are many ways of how firms can engage in non-price competition to increase their market share and retain their customer base.
Examples are such like loyalty programs, subsidized delivery, unique selling points, brand recognition, ethical and/or charitable concerns, after-sales service, positive feedback reviews, marketing campaigns and many more.
Supermarkets such as Tesco and Costco are offering delivery services worldwide as well, to cater for their international customer bases.
Firms with unique selling points are a result of focused differentiation because products are customized to consumer preferences.
[7] Such methods are important because it gives other new consumers an anchor to base the quality of their products on, and creates a certain level of trust from the amount of positive feedback received.
Examples are such like Apple Care offering warranty and also proper services to repair the purchased devices.
If advertising costs are higher than the revenues of the firms, then it would lead to a waste of resources, resulting in negative profits.
Non-price competition however, seeks to change its demographics and shape of the demand curve by adapting and innovating.
[11] The fixing of commission rates by the New York Exchange still allows brokerage houses to compete through non-price measures through offering advisory services regarding investments.
This would give each firm a fixed share of total output at the common price, therefore, showing a negatively-sloping demand curve.
[10] For cases with price regulation, antitrust policies have managed to prevent various firms within the airline industry from merging so they would still engage in non-price competition.
For cases involving third-party payors, partial solutions where consumers are forced to engage in some price comparisons where a threat of rate increases if too many claims are made.
For example, in strategic management, areas of focus revolve around continuous innovation, synergism and long-term relationships that build sustainable businesses.
A significant issue in the Continental Can litigation was how a relevant product market should be known for reviewing company mergers.