Nor'easter
They tend to develop most often and most powerfully between the months of November and March, because of the difference in temperature between the cold polar air mass coming down from central Canada and the warm ocean waters off the upper East Coast.
The term "nor'easter" naturally developed from the historical spellings and pronunciations of the compass points and the direction of wind or sailing.
[citation needed] As noted in a January 2006 editorial by William Sisson, editor of Soundings magazine,[9] use of "nor'easter" to describe the storm system is common along the U.S. East Coast.
Yet it has been asserted by linguist Mark Liberman (see below) that "nor'easter" as a contraction for "northeaster" has no basis in regional New England dialect; the Boston accent would elide the "R": no'theastuh'.
[citation needed] For decades, Edgar Comee, of Brunswick, Maine, waged a determined battle against use of the term "nor'easter" by the press, which usage he considered "a pretentious and altogether lamentable affectation" and "the odious, even loathsome, practice of landlubbers who would be seen as salty as the sea itself".
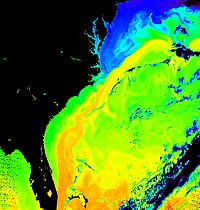
Very cold and dry air rushing southward and meeting up with the warm Gulf stream current, which is typically near 70 °F (21 °C) even mid-winter, often causes low-pressure areas to develop and intensify.
On occasion, nor'easters can pull cold air as far south as Virginia or North Carolina, bringing wet snow inland in those areas for a brief time.
[23] Such a storm will rapidly intensify, tracking northward and following the topography of the East Coast, sometimes continuing to grow stronger during its entire existence.
Type B storms form from a parent low-pressure system over the Ohio Valley, which then undergoes a center reformation over Gulf Stream off North Carolina or Virginia.
These storms can bring a swath of wintry precipitation from the Great Plains and the Ohio River Valley to the Middle Atlantic and New England.
Temperatures usually fall significantly due to the presence of the cooler air from winds that typically come from a northeasterly direction.
While this formation occurs in many places around the world, nor'easters are unique for their combination of northeast winds and moisture content of the swirling clouds.
In Europe, similar weather systems with such severity are hardly possible; the moisture content of the clouds is usually not high enough to cause flooding or heavy snow, although northeasterly winds can be strong.
Biologists at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution on Cape Cod have determined nor'easters are an environmental factor for red tides on the Atlantic coast.