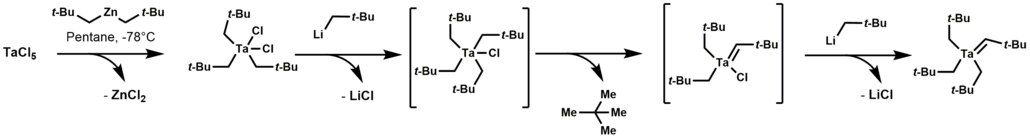
Organotantalum chemistry
This reaction initially forms a thermally unstable tetraalkyl-monochloro-tantalum complex, which undergoes α-hydrogen elimination, followed by alkylation of the remaining chloride.
Ethylene, propylene, and styrene react with tantalum alkylidene complexes to yield olefin metathesis products.
Organotantalum compounds are invoked as intermediates in C-alkylation of secondary amines with 1-alkenes using Ta(NMe2)5.
[12] The chemistry developed by Maspero was later brought to fruition when Hartwig and Herzon reported the hydroaminoalkylation of olefins to form alkylamines:[13] The catalytic cycle may proceed by β-hydrogen abstraction of the bisamide, which forms the metallaaziridine.
Subsequent olefin insertion, protonolysis of the tantalum-carbon bond, and β-hydrogen abstraction affords the alkylamine product.