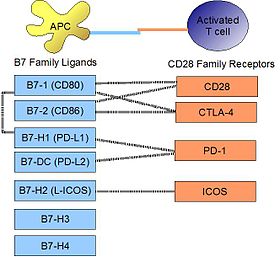
PD-L1
[5] Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a 40kDa type 1 transmembrane protein that has been speculated to play a major role in suppressing the adaptive arm of immune systems during particular events such as pregnancy, tissue allografts, autoimmune disease and other disease states such as hepatitis.
However, the exact roles of PD-L1 on hematopoietic versus nonhematopoietic cells in modulating immune responses are unclear.
[9] In 2003, B7-H1 was shown to be expressed on myeloid cells as checkpoint protein and was proposed as potential target in cancer immunotherapy in human clinic.
Said et al. showed that PD-1, up-regulated on activated CD4 T-cells, can bind to PD-L1 expressed on monocytes and induces IL-10 production by the latter.
PD-L1 binding to PD-1 also contributes to ligand-induced TCR down-modulation during antigen presentation to naive T cells, by inducing the up-regulation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase CBL-b.
In the mouse, it has been shown that classically activated macrophages (induced by type I helper T cells or a combination of LPS and interferon-gamma) greatly upregulate PD-L1.
[19] Resting human cholangiocytes express PD-L1 mRNA, but not the protein, due to translational suppression by microRNA miR-513.
In this way, interferon-gamma can induce PD-L1 protein expression by inhibiting gene-mediated suppression of mRNA translation.
In order to anticipate the effectiveness of gene therapy or systemic immunotherapy in blocking the PD-1 and PD-L1 checkpoints, PD-L1 might be employed as a prognostic marker and a target for anti-cancer immunity.
In cancer, loss of feedback restriction between transcription factors can lead to increased local PD-L1 expression, which could limit the effectiveness of systemic treatment with agents targeting PD-L1.
[36] In humans, PD-L1 was found to have altered expression in pediatric patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
In contrast, both mDC and monocytes from patients with active SLE failed to upregulate PD-L1 over a 5-day time course, expressing this protein only during disease remissions.