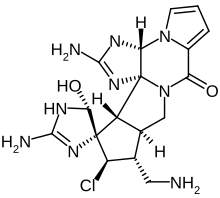
Palau'amine
Palau'amine is a toxic chlorinated alkaloid compound synthesized naturally by certain species of sea sponges.
The name of the molecule derives from the island nation of Palau, near where the first sponge species discovered to produce it, Stylotella agminata, is found.
[1] The substance was first isolated from Stylotella agminata, a sponge found in the southwest Pacific Ocean, and described in 1993.
The precise atomic structure was pinned down in 2007,[3] and two years later, the molecule was synthesized in the lab of Phil Baran at the Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, California.
[6] Based on the hypothesized biosynthesis of palau'amine, a proposed pathway to this dimeric pyrrole-imidazole alkaloid includes a key oxidation of a β-ketoester with manganese(III) acetate to initiate a cascade radical cyclization, producing an ageliferin skeleton.