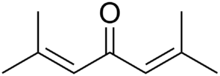
Phorone
Phorone, or diisopropylidene acetone, is a yellow crystalline substance with a geranium odor, with formula C9H14O or ((CH3)2C=CH)2C=O.
It was first obtained in 1837 in impure form by the French chemist Auguste Laurent, who called it "camphoryle".
[1] In 1849, the French chemist Charles Frédéric Gerhardt and his student Jean Pierre Liès-Bodart prepared it in a pure state and named it "phorone".
[2] On both occasions it was produced by ketonization through the dry distillation of the calcium salt of camphoric acid.
[3][4] It is now typically obtained by the acid-catalysed twofold aldol condensation of three molecules of acetone.