Pump
Positive-displacement pumps, unlike centrifugal, can theoretically produce the same flow at a given rotational speed no matter what the discharge pressure.
[4] Advantages: Rotary pumps are very efficient[5] because they can handle highly viscous fluids with higher flow rates as viscosity increases.
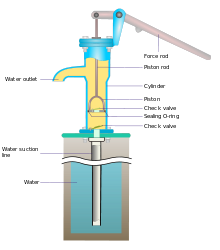
In order for suction to take place, the pump must first pull the plunger in an outward motion to decrease pressure in the chamber.
The volume is constant given each cycle of operation and the pump's volumetric efficiency can be achieved through routine maintenance and inspection of its valves.
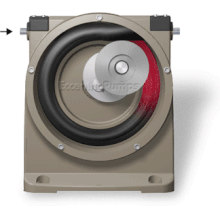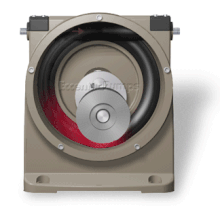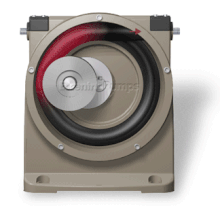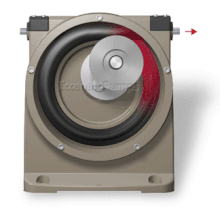
This can be visualized as a central core of diameter x with, typically, a curved spiral wound around of thickness half x, though in reality it is manufactured in a single casting.
Additionally, when the tube opens to its natural state after the passing of the cam it draws (restitution) fluid into the pump.
In 1968, William Bruggeman reduced the size of the triplex pump and increased the lifespan so that car washes could use equipment with smaller footprints.
Industrial-grade or continuous duty triplex pumps on the other end of the quality spectrum may run for as much as 2,080 hours a year.
[18] Drillers use triplex or even quintuplex pumps to inject water and solvents deep into shale in the extraction process called fracking.
Conventional impulse pumps include: Instead of a gas accumulation and releasing cycle, the pressure can be created by burning of hydrocarbons.
Dynamic pumps differ in that they can be safely operated under closed valve conditions (for short periods of time).
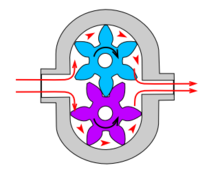
The fluid enters along the axis or center, is accelerated by the impeller and exits at right angles to the shaft (radially); an example is the centrifugal fan, which is commonly used to implement a vacuum cleaner.
[27][28][29] As regenerative turbine pumps cannot become vapor locked, they are commonly applied to volatile, hot, or cryogenic fluid transport.
Recently there has been a resurgence of interest in low-power solar steam pumps for use in smallholder irrigation in developing countries.
In fact, many fluid-dynamical systems in nature and engineering more or less rely upon valveless pumping to transport the working fluids therein.
Meanwhile, the embryonic vertebrate heart begins pumping blood long before the development of discernible chambers and valves.
The pump chamber is emptied through the printing jet due to reduced flow impedance in that direction and refilled by capillary action.
[32] In early 2005, Gordon Buck, John Crane Inc.'s chief engineer for field operations in Baton Rouge, Louisiana, examined the repair records for a number of refinery and chemical plants to obtain meaningful reliability data for centrifugal pumps.
In some cases, the alliance contract included having a John Crane Inc. technician or engineer on-site to coordinate various aspects of the program.
Things have improved in recent years, but the somewhat restricted space available in "old" DIN and ASME-standardized stuffing boxes places limits on the type of seal that fits.
Unscheduled maintenance is often one of the most significant costs of ownership, and failures of mechanical seals and bearings are among the major causes.
Modern hand-operated community pumps are considered the most sustainable low-cost option for safe water supply in resource-poor settings, often in rural areas in developing countries.
A hand pump opens access to deeper groundwater that is often not polluted and also improves the safety of a well by protecting the water source from contaminated buckets.
Multiphase pumping applications, also referred to as tri-phase, have grown due to increased oil drilling activity.
In essence, the multiphase pump can accommodate all fluid stream properties with one piece of equipment, which has a smaller footprint.
The buffer tank breaks the energy of the liquid slug, smooths any fluctuations in the incoming flow and acts as a sand trap.
The head can be simplified as the number of feet or metres the pump can raise or lower a column of water at atmospheric pressure.
From an initial design point of view, engineers often use a quantity termed the specific speed to identify the most suitable pump type for a particular combination of flow rate and head.
Hence the power, P, required by the pump: where Δp is the change in total pressure between the inlet and outlet (in Pa), and Q, the volume flow-rate of the fluid is given in m3/s.
Pump efficiencies tend to decline over time due to wear (e.g. increasing clearances as impellers reduce in size).