Ionizing radiation
[4] Ionizing radiation is used in a wide variety of fields such as medicine, nuclear power, research, and industrial manufacturing, but is a health hazard if proper measures against excessive exposure are not taken.
In the atmosphere such particles are often stopped by air molecules, and this produces short-lived charged pions, which soon decay to muons, a primary type of cosmic ray radiation that reaches the surface of the earth.
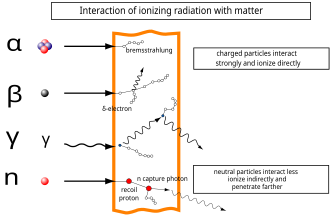
Alpha particles are a strongly ionizing form of radiation, but when emitted by radioactive decay they have low penetration power and can be absorbed by a few centimeters of air, or by the top layer of human skin.
The helium nuclei that form 10–12% of cosmic rays, are also usually of much higher energy than those from radioactive decay and pose shielding problems in space.
[7] The alpha particle was named by Ernest Rutherford after the first letter in the Greek alphabet, α, when he ranked the known radioactive emissions in descending order of ionizing effect in 1899.
High-energy beta particles may produce X-rays known as bremsstrahlung ("braking radiation") or secondary electrons (delta ray) as they pass through matter.
In space, however, very high energy protons, helium nuclei, and HZE ions can be initially stopped by relatively thin layers of shielding, clothes, or skin.
However, US Federal Communications Commission material defines ionizing radiation as that with a photon energy greater than 10 eV (equivalent to a far ultraviolet wavelength of 124 nanometers).
This high-energy β− further interacts rapidly with other nuclei, emitting high-energy γ via BremsstrahlungWhile not a favorable reaction, the 16O (n,p) 16N reaction is a major source of X-rays emitted from the cooling water of a pressurized water reactor and contributes enormously to the radiation generated by a water-cooled nuclear reactor while operating.
In fissile materials, secondary neutrons may produce nuclear chain reactions, causing a larger amount of ionization from the daughter products of fission.
Ionization of molecules can lead to radiolysis (breaking chemical bonds), and formation of highly reactive free radicals.
This is a particular hazard in semiconductor microelectronics used in electronic equipment; subsequent currents introduce operation errors or even permanently damage the devices.
Devices intended for high-radiation environments such as the nuclear industry or outer space, may be made radiation hard to resist such effects through design, material selection, and fabrication methods.
Thus, the mid and lower ultraviolet electromagnetic spectrum is damaging to biological tissues as a result of electronic excitation in molecules which falls short of ionization, but produces similar non-thermal effects.
The penetrating power of x-ray, gamma, beta, and positron radiation is used for medical imaging, nondestructive testing, and a variety of industrial gauges.
The highest level of purely natural radiation recorded on the Earth's surface is 90 μGy/h (0.8 Gy/a) on a Brazilian black beach composed of monazite.
[28] The highest background radiation in an inhabited area is found in Ramsar, mainly due to naturally radioactive limestone used as a building material.
Some 2000 of the most exposed residents receive an average radiation dose of 10 mGy per year, (1 rad/yr) ten times more than the ICRP recommended limit for exposure to the public from artificial sources.
Despite the high levels of background radiation that the residents of Ramsar receive there is no compelling evidence that they experience a greater health risk.
Airline crews receive more cosmic rays if they routinely work flight routes that take them close to the North or South pole at high altitudes, where this type of radiation is maximal.
An important source of natural radiation is radon gas, which seeps continuously from bedrock but can, because of its high density, accumulate in poorly ventilated houses.
For human-made sources the use of Containment is a major tool in reducing dose uptake and is effectively a combination of shielding and isolation from the open environment.
Work rooms, hot cells and gloveboxes have slightly reduced air pressures to prevent escape of airborne material to the open environment.
One is the issue of potassium iodide (KI) tablets, which blocks the uptake of radioactive iodine (one of the major radioisotope products of nuclear fission) into the human thyroid gland.
Occupationally exposed individuals are controlled within the regulatory framework of the country they work in, and in accordance with any local nuclear licence constraints.
), televisions, luminous watches and dials (tritium), airport X-ray systems, smoke detectors (americium), electron tubes, and gas lantern mantles (thorium).
The International Commission on Radiological Protection recommends limiting artificial irradiation to the public to an average of 1 mSv (0.001 Sv) of effective dose per year, not including medical and occupational exposures.
Highly charged HZE ions in particular are known to be extremely damaging, though protons make up the vast majority of galactic cosmic rays.
[35] Air travel exposes people on aircraft to increased radiation from space as compared to sea level, including cosmic rays and from solar flare events.
[37] The United States FAA requires airlines to provide flight crew with information about cosmic radiation, and an International Commission on Radiological Protection recommendation for the general public is no more than 1 mSv per year.