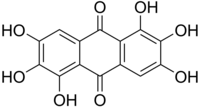
Rufigallol
It occurs naturally being derived from gallic acid.
The compound is soluble in dioxane, from which it crystallizes as red needles that sublime without melting at 365 °C.
[1] It is prepared by acid-catalyzed condensation of a pair of gallic acid molecules.
[2] Rufigallol is particularly toxic to the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum and has a synergistic effect in combination with the antimalarial drug exifone, which has structural similarities to rufigallol.
[3] Rufigallol forms a crimson-colored complex with beryllium, aluminium, thorium, zirconium and hafnium, and this reaction has been used for the spot and spectrophotometric determination of beryllium in low concentrations.