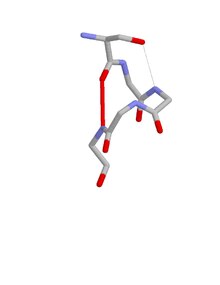
ST motif
The ST motif is a commonly occurring feature in proteins and polypeptides.
When one of the hydrogen bonds is between the side chain oxygen of residue i and the main chain NH of residue i + 2 the motif incorporates an ST turn.
Two well conserved threonines at α-helical N-termini occur as ST motifs and form part of the characteristic nucleotide binding sites of SF1 and SF2 type DNA and RNA helicases.
[12] It has been suggested that the sequences SPXX or STXX are frequently found at DNA-binding sites and also that they are recognized as substrates by some protein kinases.
Structural studies of polypeptides indicate that such tetrapeptides can adopt the hydrogen bonding pattern of the ST motif.