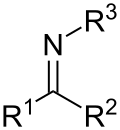
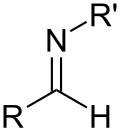
Schiff base
[4] Schiff bases can be synthesized from an aliphatic or aromatic amine and a carbonyl compound by nucleophilic addition forming a hemiaminal, followed by a dehydration to generate an imine.
Schiff bases have been investigated in relation to a wide range of contexts, including antimicrobial, antiviral and anticancer activity.
[6] Schiff bases are common enzymatic intermediates where an amine, such as the terminal group of a lysine residue, reversibly reacts with an aldehyde or ketone of a cofactor or substrate.
The common enzyme cofactor pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) forms a Schiff base with a lysine residue and is transaldiminated to the substrate(s).
The term Schiff base is normally applied to these compounds when they are being used as ligands to form coordination complexes with metal ions.