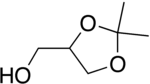
Solketal
Solketal has been used extensively in the synthesis of mono-, di- and triglycerides by ester bond formation.
The free hydroxyl group of solketal can be esterified with a carboxylic acid to form the protected monoglyceride.
The isopropylene group can then be removed using an acid catalyst in aqueous or alcoholic medium.
The unprotected diol can then be esterified further to form either the di- or triglyceride.
Another route to specific di- or triglycerides involves converting the solketal to glycidol (2,3-epoxy-1-propanol) and esterifying this with one fatty acid before opening the epoxy by heating in the presence of a second fatty acid and a catalyst.