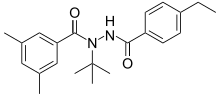
Tebufenozide
[3] Because it has high selectivity for the targeted pests and low toxicity otherwise, the company that discovered tebufenozide, Rohm and Haas, was given a Presidential Green Chemistry Award for its development.
Tebufenozide is the active ingredient in" Bayer's MIMIC formulation, which controls forest defoliator pests such as gypsy moths, tent caterpillars, budworms, tussock moths and cabbage looper.
[6] In California, the substance was used chiefly for crops of head lettuce, celery, raspberries, cauliflower, and tomatoes for processing.
A 1994 study conducted by the Canadian Forest Service in laboratory conditions concluded that the substance was very stable in acidic and neutral buffers at 20 °C, hydrolytic degradation was dependent on pH and temperature, sunlight photodegradation was observed at a slower rate than ultraviolet photodegradation, and that microbial metabolism and photolysis are the two main degradative routes for tebufenozide in natural aquatic systems.
[7] The final degradation products of tebufenozide are various alcohols, carboxylic acids and ketones of low toxicity.