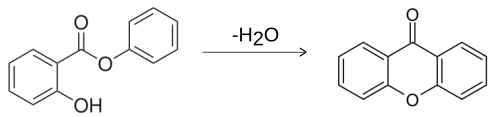
Xanthone
Xanthone is an organic compound with the molecular formula C13H8O2.
In 1939, xanthone was introduced as an insecticide and it currently finds uses as ovicide for codling moth eggs and as a larvicide.
[2] Xanthone is also used in the preparation of xanthydrol, which is used in the determination of urea levels in the blood.
Many are phytochemicals found in plants in the families Bonnetiaceae, Clusiaceae, and Podostemaceae.
[8] Some xanthones are found in the pericarp of the mangosteen fruit (Garcinia mangostana) as well as in the bark and timber of Mesua thwaitesii.