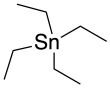
Tetraethyltin
Tetraethyltin or tetraethyl tin is a chemical compound with the formula (CH3CH2)4Sn, that is, a tin atom attached to four ethyl groups.
It is an important example of an organotin compound, often abbreviated as TET.
Tetraethyltin is a colourless flammable liquid, soluble in diethyl ether and insoluble in water, that freezes at −112 °C and boils at 181 °C.
Tetraethyltin can be obtained by reacting ethylmagnesium bromide with tin(IV) chloride:[1] The same reaction can be used to obtain tetra-n-propyltin and tetra-n-butyltin.
[1] Tetraethyltin is converted in the body to the more toxic triethylstannylium ions.