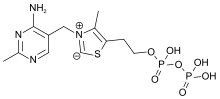
Thiamine pyrophosphate
Thiamine pyrophosphate is a cofactor that is present in all living systems, in which it catalyzes several biochemical reactions.
[2][3][4] It was first discovered as an essential nutrient (vitamin) in humans through its link with the peripheral nervous system disease beriberi, which results from a deficiency of thiamine in the diet.
[5] TPP works as a coenzyme in many enzymatic reactions, such as: Chemically, TPP consists of a pyrimidine ring which is connected to a thiazole ring, which is in turn connected to a pyrophosphate (diphosphate) functional group.
The part of TPP molecule that is most commonly involved in reactions is the thiazole ring, which contains nitrogen and sulfur.
[5][8] In several reactions, including that of pyruvate dehydrogenase, alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, and transketolase, TPP catalyses the reversible decarboxylation reaction (aka cleavage of a substrate compound at a carbon-carbon bond connecting a carbonyl group to an adjacent reactive group—usually a carboxylic acid or an alcohol).