Trans-acting siRNA
[1][2] Initial descriptions found involvement of the plant protein suppressor of gene silencing 3 (SGS3), and the enzyme RNA-dependant RNA polymerase 6 (RDR6).
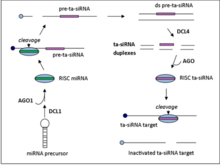
Ta-siRNAs are generated from non-coding transcripts through Argonaute-mediated miRNA-guided cleavage followed by conversion to double stranded RNA by RDR6.
[5] The resulting dsRNA is further processed by dicer-like enzyme 4 (DCL4) to produce a phased array of 21-nt siRNAs from positions adjoining the miRNA cleavage site.
RDR6 then converts the transcript into a double strand RNA fragment which then gets processed by DCL4 to generate the 21-nt siRNA with 2 nucleotide 3’ overhangs that target complementary mRNAs in trans.
[1][2][8] A member of the Argonaute protein family is a component of all RNA silencing effector complexes, including the RISCs that catalyze mRNA cleavage.
[10] In addition to being present in A. thaliana,[6] evidence of ta-siRNAs has also been found in the moss Physcomitrella patens,[5] maize,[11] Oryza sativa (rice),[12] and other plants.