Neoplasm
The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed.
[3] The word neoplasm is from Ancient Greek νέος- neo 'new' and πλάσμα plasma 'formation, creation'.
In modern English, tumor (non-US spelling: tumour) is used as a synonym for a neoplasm (a solid or fluid-filled cystic lesion that may or may not be formed by an abnormal growth of neoplastic cells) that appears enlarged in size.
Generally speaking, however, the term tumor is used generically, without reference to the physical size of the lesion.
[16] Under this type of model, mechanical stresses and strains can be dealt with and their influence on the growth of the tumor and the surrounding tissue and vasculature elucidated.
[17] Benign conditions that are not associated with an abnormal proliferation of tissue (such as sebaceous cysts) can also present as tumors, however, but have no malignant potential.
Breast cysts (as occur commonly during pregnancy and at other times) are another example, as are other encapsulated glandular swellings (thyroid, adrenal gland, pancreas).
[citation needed] Discrete localized enlargements of normal structures (ureters, blood vessels, intrahepatic or extrahepatic biliary ducts, pulmonary inclusions, or gastrointestinal duplications) due to outflow obstructions or narrowings, or abnormal connections, may also present as a tumor.
It can be dangerous to biopsy a number of types of tumor in which the leakage of their contents would potentially be catastrophic.
[citation needed] DNA damage is considered to be the primary underlying cause of malignant neoplasms known as cancers.
[21] Helicobacter pylori infection produces high levels of reactive oxygen species that damage DNA and contributes to gastric cancer.
[28][29][30][31][32] Similarly, out of 119 cases of mismatch repair-deficient colorectal cancers that lacked DNA repair gene PMS2 expression, PMS2 was deficient in 6 due to mutations in the PMS2 gene, while in 103 cases PMS2 expression was deficient because its pairing partner MLH1 was repressed due to promoter methylation (PMS2 protein is unstable in the absence of MLH1).
[34] In further examples, epigenetic defects were found at frequencies of between 13%-100% for the DNA repair genes BRCA1, WRN, FANCB, FANCF, MGMT, MLH1, MSH2, MSH4, ERCC1, XPF, NEIL1 and ATM.
Two or three deficiencies in expression of ERCC1, XPF or PMS2 occur simultaneously in the majority of the 49 colon cancers evaluated by Facista et al.[35] Epigenetic alterations causing reduced expression of DNA repair genes is shown in a central box at the third level from the top of the figure in this section, and the consequent DNA repair deficiency is shown at the fourth level.
[46] Similarly, Vogelstein et al.[47] point out that more than half of somatic mutations identified in tumors occurred in a pre-neoplastic phase (in a field defect), during growth of apparently normal cells.
Likewise, epigenetic alterations present in tumors may have occurred in pre-neoplastic field defects.
[citation needed] An expanded view of field effect has been termed "etiologic field effect", which encompasses not only molecular and pathologic changes in pre-neoplastic cells but also influences of exogenous environmental factors and molecular changes in the local microenvironment on neoplastic evolution from tumor initiation to patient death.
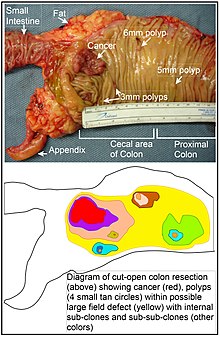
These neoplasms are also indicated, in the diagram below the photo, by 4 small tan circles (polyps) and a larger red area (cancer).
[citation needed] If the general process by which sporadic colon cancers arise is the formation of a pre-neoplastic clone that spreads by natural selection, followed by formation of internal sub-clones within the initial clone, and sub-sub-clones inside those, then colon cancers generally should be associated with, and be preceded by, fields of increasing abnormality reflecting the succession of premalignant events.
The most extensive region of abnormality (the outermost yellow irregular area in the diagram) would reflect the earliest event in formation of a malignant neoplasm.
The Table, below, gives examples for which the DNA repair deficiency in a cancer was shown to be caused by an epigenetic alteration, and the somewhat lower frequencies with which the same epigenetically caused DNA repair deficiency was found in the surrounding field defect.
Some of the small polyps in the field defect shown in the photo of the opened colon segment may be relatively benign neoplasms.
[47] However, the average number of DNA sequence mutations in the entire genome (including non-protein-coding regions) within a breast cancer tissue sample is about 20,000.
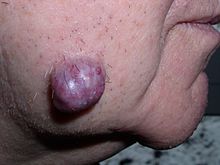
[citation needed] In its medical sense, tumor has traditionally meant an abnormal swelling of the flesh.
The Roman medical encyclopedist Celsus (c. 30 BC–38 AD) described the four cardinal signs of acute inflammation as tumor, dolor, calor, and rubor (swelling, pain, increased heat, and redness).