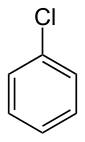
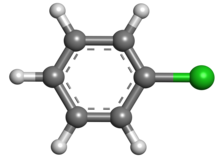
Chlorobenzene
[6] The major use of chlorobenzene is as a precursor for further intermediates such as nitrophenols, nitroanisole, chloroaniline, and phenylenediamines, which are used in the production of herbicides, dyestuffs, chemicals for rubber, and pharmaceuticals.
[7] It is also used as a high-boiling solvent in industrial and laboratory applications, for materials such as oils, waxes, resins, and rubber.
[8] The Occupational Safety and Health Administration has set a permissible exposure limit at 75 ppm (350 mg/m3) over an eight-hour time-weighted average for workers handling chlorobenzene.
The bacterium Rhodococcus phenolicus degrades chlorobenzene, dichlorobenzene and phenol as sole carbon sources.
[12] Upon entering the body, typically via contaminated air, chlorobenzene is excreted both via the lungs and the urinary system.