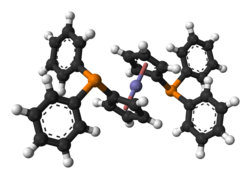
1,1'-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene
It contains a ferrocene moiety in its backbone, and is related to other bridged diphosphines such as 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (dppe).
It may be prepared by treating dilithioferrocene with chlorodiphenylphosphine:[1] The dilithiation of ferrocene is easily achieved with n-butyllithium in the presence of TMEDA.
The Fe center is typically not involved in the behavior of the ligand.
[2] The palladium derivative, (dppf)PdCl2, which is popular for palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions, is prepared by treating dppf with the acetonitrile or benzonitrile adducts of palladium dichloride:[2] Substitution of the phenyl substituents in dppf leads to derivatives with modified donor-acceptor properties at the phosphorus atoms.
It promotes the amination of aryl chlorides, sulfamates, mesylates, and triflates.