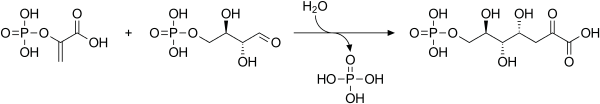3-Deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonic acid 7-phosphate
The mechanism of ring closure is complex, but involves an aldol condensation at C-2 and C-7.
[1] The first step, condensation of 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonic acid 7-phosphate (DAHP) from PEP/E4P, uses three isoenzymes AroF, AroG, and AroH.
These isoenzymes all have the ability to help regulate synthesis of DAHP by the method of feedback inhibition.
This acts in the cell by monitoring the concentrations of each of the three aromatic amino acids.
With the first step of the common pathway shut off, synthesis of the three amino acids can not proceed.