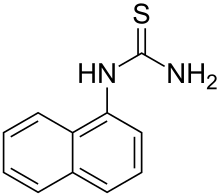
α-Naphthylthiourea
Naphthylthiourea is available as 10% active baits in suitable protein- or carbohydrate-rich materials and as a 20% tracking powder.
In ANTU poisoning plasma, carbon and ferritin escape through a gap in the thick part of the pulmonary capillary into the interstitial tissues of the lung[10] Alpha-Naphthylthiourea is toxic to inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact, although the intoxication may be delayed.
According to the U.S. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), the recommended workplace airborne exposure limit is 0.3 mg/m3 averaged over a 10-hour workshift.
[15] Superoxide dismutase, catalase and dimethylsulfoxide all protect against the lung damage by ANTU (although the results are diverse).
Given hydroxyurea over two days does not block the ANTU damage when neutrophils are decreased or when administered acutely.
Cyclooxygenase pathway may generate the free radicals since ibuprofen blocked as well the ANTU damage.
In the most cases a pale, mottled liver and damaged kidneys are found in animals which have ingested ANTU.
[27] In a long-term, ANTU may cause pulmonary edema and pleural effusion in certain animals, such as rats.
There are subproducts of this reaction which play an important role in toxicity: atomic sulfur and a metabolic reactive containing the carbon carbonyl of ANTU.
[29] ANTU was developed to combat infestation of rats in the US city of Baltimore, where the increase in population had overwhelmed the sanitation services, causing huge rat-infested garbage piles.
However, when Richter started testing the compound in wild rats, it was not equally tasteless for them, but had a bitter taste; Richter's lab screened over 200 thiourea compounds to find one equally tasteless and toxic to wild rats.
The ANTU field trials soon expanded and in 1943 Richter was asked to lead citywide rat control campaign and received funding to replace the Scouts with adult baiters and trappers.
The city of Baltimore soon returned to an environmental approach in rat control and ANTU disappeared from the market after a few years.