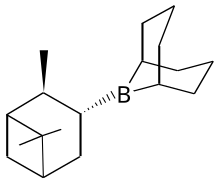
Alpine borane
[3] Hydrolysis of the resulting borinic ester affords the alcohol: It is also effective for the stereoselective reduction of certain acetylenic ketones.
[4] The reaction is proposed to involve formation of an adduct by coordination of the carbonyl oxygen to boron.
Intramolecular hydride transfer from the pinane substituent to the carbonyl carbon ensues.
Many substrates for the Midland reduction have a low steric group such as an alkyne[5] or a nitrile[6] so as to increase selectivity.
Stereochemical control comes from coordination of the carbonyl bulky borane, followed by hydride transfer opposite the largest group.