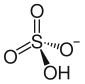
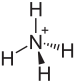Ammonium bisulfate
This salt is the product of the half-neutralization of sulfuric acid by ammonia.
It is commonly collected as a byproduct of the "acetone cyanohydrin route" to the commodity chemical methyl methacrylate.
[1] It can also be obtained by hydrolysis of sulfamic acid in aqueous solution, which produces the salt in high purity: It also arises by the thermal decomposition of ammonium sulfate: It can be further neutralized with ammonia to form ammonium sulfate, a valuable fertilizer.
It can be used as a weaker alternative to sulfuric acid, although sodium bisulfate is much more common.
A related compound of the (NH4)3H(SO4)2 formula, occurs as the rare mineral letovicite, known from coal fire environments.