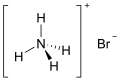
Ammonium bromide
The chemical crystallizes in colorless prisms, possessing a saline taste; it sublimes on heating and is easily soluble in water.
On exposure to air it gradually assumes a yellow color because of the oxidation of bromide (Br−) to bromine (Br2).
Ammonium bromide is a weak acid with a pKa of approximately 9 in water.
It is an acid salt because the ammonium ion hydrolyzes slightly in water.
Ammonium bromide is a strong electrolyte when put in water: Ammonium bromide decomposes to ammonia and hydrogen bromide when heated at elevated temperatures: Ammonium bromide is used for photography in films, plates and papers; in fireproofing of wood; in lithography and process engraving; in corrosion inhibitors; and in pharmaceutical preparations.