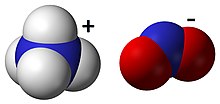
Ammonium nitrite
It is not used in pure isolated form since it is highly unstable and decomposes into water and nitrogen, even at room temperature.
Ammonium nitrite forms naturally in the air and can be prepared by the absorption of equal parts nitrogen dioxide and nitric oxide in aqueous ammonia.
Ammonium nitrite may explode at a temperature of 60–70 °C,[1] and will decompose quicker when dissolved in a concentrated aqueous solution, than in the form of a dry crystal.
[2] Ammonium nitrite solution is stable at higher pH and lower temperature.
If there is any decrease in pH lower than 7.0, it may lead to an explosion, since the nitrite can react to it.