Ammonium paratungstate
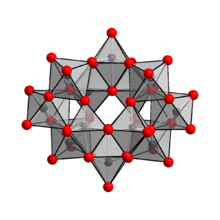
Ammonium paratungstate (or APT) is a white crystalline salt with the chemical formula (NH4)10(H2W12O42)·4H2O.
"[2] Tungsten ores, which are typically oxides, are digested in base to give solutions of tungstate together with many contaminating species.
This crude extract is acidified and treated with sulfide to separate molybdenum trisulfide.
Heating ammonium paratungstate to its decomposition temperature of 600 °C yields tungsten(VI) oxide, as described in this idealized equation: From there, the trioxide is heated in an atmosphere of hydrogen, yielding elemental tungsten:[3] The anion in (NH4)10(W12O41)·5H2O has been shown to be [H2W12O42]10−, containing two hydrogen atoms, keeping two hydrogen atoms inside the cage.
Gibbs remarked about this: When concentrating an ammoniacal solution of tungstic acid (i.e. hydrous WO3), the product obtained is ammonium paratungstate.